7 Common Engine Performance Problems and How to Fix Them

Experiencing engine performance issues? This guide covers 7 common problems, including misfires, rough idling, and power loss, along with troubleshooting steps and solutions. Diagnose and fix common engine problems quickly and effectively.
Understanding Engine Misfires and Misfire Troubleshooting
Engine misfires are a frustrating and often perplexing problem for car owners. A misfire occurs when one or more cylinders in your engine fail to ignite the air-fuel mixture properly. This can lead to a noticeable loss of power, rough idling, poor fuel economy, and even damage to your engine if left unchecked. But what causes misfires, and how can you diagnose and fix them?
Causes of Engine Misfires:
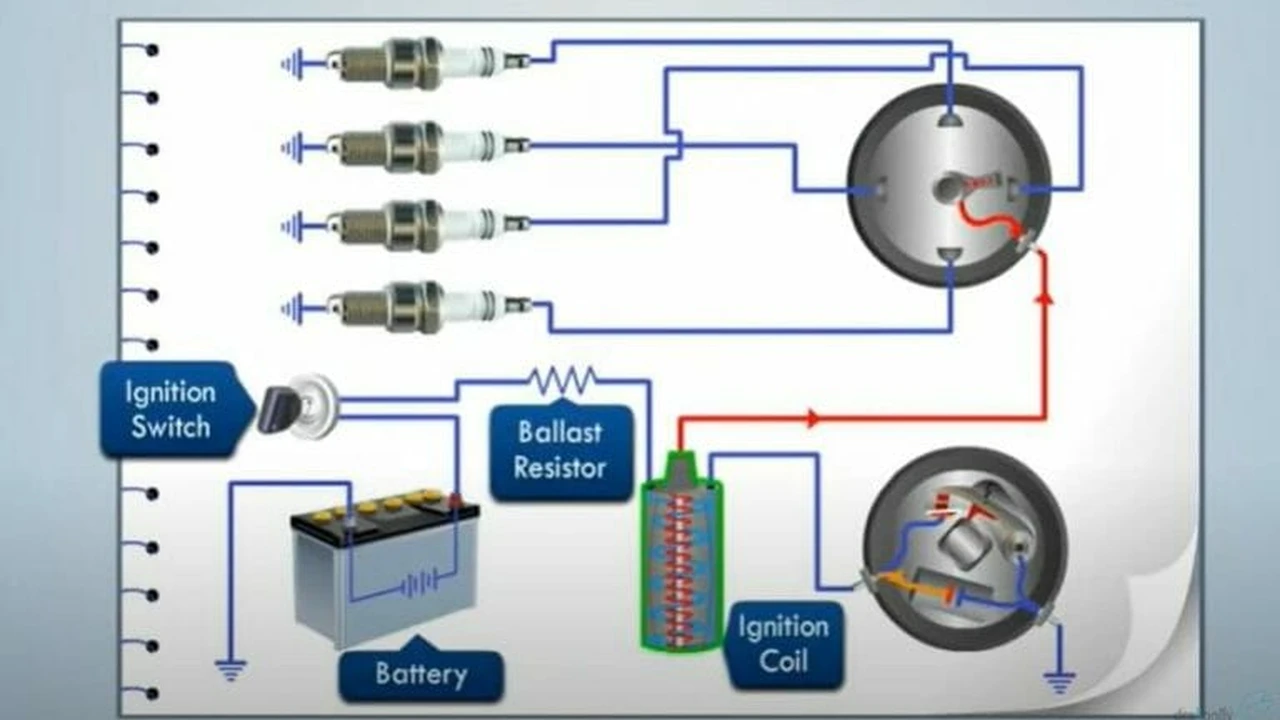
- Faulty Spark Plugs: Spark plugs are responsible for igniting the air-fuel mixture in the cylinders. Worn, cracked, or improperly gapped spark plugs can fail to produce a strong enough spark, leading to misfires.
- Failing Ignition Coils: Ignition coils provide the high voltage needed to fire the spark plugs. A failing ignition coil can result in a weak or intermittent spark, causing misfires.
- Vacuum Leaks: Vacuum leaks allow unmetered air into the engine, disrupting the air-fuel mixture and leading to misfires, especially at idle.
- Clogged Fuel Injectors: Clogged fuel injectors restrict fuel flow to the cylinders, resulting in a lean air-fuel mixture and misfires.
- Low Compression: Low compression in a cylinder can prevent the air-fuel mixture from igniting properly, leading to misfires. This can be caused by worn piston rings, damaged valves, or a blown head gasket.
- Faulty Sensors: Sensors like the Mass Airflow (MAF) sensor or Oxygen (O2) sensor can provide incorrect data to the engine control unit (ECU), leading to improper fuel delivery and misfires.
- Timing Issues: Incorrect engine timing can cause misfires, as the spark plugs may fire at the wrong time in the combustion cycle.
Symptoms of Engine Misfires:
- Rough Idling: The engine may shake or vibrate excessively at idle.
- Loss of Power: The car may feel sluggish and accelerate slowly.
- Poor Fuel Economy: Misfires can reduce fuel efficiency.
- Check Engine Light: The check engine light will often illuminate when a misfire is detected.
- Hesitation or Stumbling: The engine may hesitate or stumble during acceleration.
- Unusual Noises: You may hear popping or sputtering noises from the exhaust.
Diagnosing and Fixing Engine Misfires:
- Read the OBD2 Codes: Use an OBD2 scanner to retrieve the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the ECU. These codes can provide valuable clues about the cause of the misfire. Common misfire codes include P0300 (Random Misfire), P0301 (Misfire Cylinder 1), P0302 (Misfire Cylinder 2), etc.
- Inspect Spark Plugs: Remove and inspect the spark plugs for wear, damage, or improper gapping. Replace any faulty spark plugs with the correct type for your vehicle.
- Test Ignition Coils: Use a multimeter to test the resistance of the ignition coils. A faulty ignition coil will typically have a significantly different resistance reading than the others. Replace any faulty ignition coils.
- Check for Vacuum Leaks: Inspect vacuum hoses and intake gaskets for cracks or leaks. You can use a vacuum gauge or a smoke machine to help locate vacuum leaks. Repair or replace any leaking components.
- Clean or Replace Fuel Injectors: If you suspect clogged fuel injectors, you can try cleaning them with a fuel injector cleaner. If cleaning doesn't work, you may need to replace the injectors.
- Perform a Compression Test: A compression test can help determine if there is low compression in any of the cylinders. If you find low compression, you may need to perform further diagnosis to determine the cause (e.g., worn piston rings, damaged valves).
- Inspect Sensors: Check the MAF sensor and O2 sensors for damage or contamination. You can use a multimeter to test the sensors' output voltage. Replace any faulty sensors.
- Check Engine Timing: Verify that the engine timing is correct. Incorrect timing can be caused by a stretched timing belt or chain, or a faulty timing belt tensioner.
Rough Idling Issues and Solutions for Engine Performance
A rough idling engine is another common complaint among car owners. It refers to an engine that vibrates, shakes, or runs unevenly when the car is stopped and the engine is idling. This can be caused by a variety of factors, and it can be both annoying and a sign of underlying engine problems. Let's explore the common causes and solutions for rough idling.
Causes of Rough Idling:
- Vacuum Leaks: As mentioned earlier, vacuum leaks can cause a rough idle by disrupting the air-fuel mixture.
- Dirty Throttle Body: A dirty throttle body can restrict airflow into the engine, leading to a rough idle.
- Faulty Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve: The IAC valve regulates airflow into the engine at idle. A faulty IAC valve can cause the engine to idle too high or too low, or to idle roughly.
- Clogged Fuel Injectors: Clogged fuel injectors can cause a lean air-fuel mixture, leading to a rough idle.
- Worn Spark Plugs: Worn spark plugs can cause misfires, which can contribute to a rough idle.
- Faulty Sensors: Sensors like the MAF sensor or O2 sensor can provide incorrect data to the ECU, leading to improper fuel delivery and a rough idle.
- Engine Mounts: Worn or damaged engine mounts can allow the engine to vibrate excessively, causing a rough idle.
Symptoms of Rough Idling:
- Engine Vibration: The engine may shake or vibrate excessively at idle.
- Fluctuating RPM: The engine RPM may fluctuate up and down at idle.
- Stalling: The engine may stall at idle.
- Hesitation or Stumbling: The engine may hesitate or stumble when accelerating from a stop.
Diagnosing and Fixing Rough Idling:
- Check for Vacuum Leaks: Inspect vacuum hoses and intake gaskets for cracks or leaks. Use a vacuum gauge or a smoke machine to help locate vacuum leaks. Repair or replace any leaking components.
- Clean the Throttle Body: Clean the throttle body with a throttle body cleaner. Remove any carbon buildup or debris that may be restricting airflow.
- Test or Replace the IAC Valve: Use a multimeter to test the resistance of the IAC valve. If the valve is faulty, replace it with a new one.
- Clean or Replace Fuel Injectors: If you suspect clogged fuel injectors, try cleaning them with a fuel injector cleaner. If cleaning doesn't work, you may need to replace the injectors.
- Inspect Spark Plugs: Remove and inspect the spark plugs for wear, damage, or improper gapping. Replace any faulty spark plugs with the correct type for your vehicle.
- Inspect Sensors: Check the MAF sensor and O2 sensors for damage or contamination. Use a multimeter to test the sensors' output voltage. Replace any faulty sensors.
- Inspect Engine Mounts: Inspect the engine mounts for cracks or damage. Replace any worn or damaged engine mounts.
Addressing Engine Power Loss and Performance Restoration
Engine power loss is a common and concerning issue that many drivers experience. It manifests as a noticeable decrease in acceleration, overall performance, and the ability to climb hills or carry heavy loads. Understanding the potential causes and knowing how to address them is crucial for maintaining your vehicle's performance and preventing further damage. Let's dive into the common reasons behind power loss and the steps you can take to restore your engine's strength.
Causes of Engine Power Loss:
- Clogged Air Filter: A clogged air filter restricts airflow into the engine, reducing power and fuel economy.
- Clogged Fuel Filter: A clogged fuel filter restricts fuel flow to the engine, leading to a lean air-fuel mixture and power loss.
- Weak Fuel Pump: A weak fuel pump may not be able to deliver enough fuel to the engine, especially under heavy load.
- Clogged Catalytic Converter: A clogged catalytic converter restricts exhaust flow, reducing power and fuel economy.
- Vacuum Leaks: Vacuum leaks disrupt the air-fuel mixture, leading to power loss.
- Low Compression: Low compression in one or more cylinders can significantly reduce engine power.
- Timing Issues: Incorrect engine timing can cause power loss.
- Faulty Sensors: Sensors like the MAF sensor or O2 sensor can provide incorrect data to the ECU, leading to improper fuel delivery and power loss.
Symptoms of Engine Power Loss:
- Reduced Acceleration: The car may feel sluggish and accelerate slowly.
- Difficulty Climbing Hills: The car may struggle to climb hills.
- Poor Fuel Economy: Power loss can reduce fuel efficiency.
- Hesitation or Stumbling: The engine may hesitate or stumble during acceleration.
Diagnosing and Fixing Engine Power Loss:
- Replace the Air Filter: Replace the air filter with a new one.
- Replace the Fuel Filter: Replace the fuel filter with a new one.
- Test the Fuel Pump: Use a fuel pressure gauge to test the fuel pump's pressure. If the pressure is low, you may need to replace the fuel pump.
- Inspect the Catalytic Converter: Inspect the catalytic converter for damage or clogging. If the converter is clogged, you may need to replace it.
- Check for Vacuum Leaks: Inspect vacuum hoses and intake gaskets for cracks or leaks. Use a vacuum gauge or a smoke machine to help locate vacuum leaks. Repair or replace any leaking components.
- Perform a Compression Test: A compression test can help determine if there is low compression in any of the cylinders. If you find low compression, you may need to perform further diagnosis to determine the cause (e.g., worn piston rings, damaged valves).
- Check Engine Timing: Verify that the engine timing is correct. Incorrect timing can be caused by a stretched timing belt or chain, or a faulty timing belt tensioner.
- Inspect Sensors: Check the MAF sensor and O2 sensors for damage or contamination. Use a multimeter to test the sensors' output voltage. Replace any faulty sensors.
Product Recommendations for Diagnosing and Repairing Engine Problems
Having the right tools and products can make diagnosing and repairing engine problems much easier. Here are some recommendations for OBD2 scanners, fuel injector cleaners, and other helpful products:
OBD2 Scanners for Engine Diagnostics and Code Reading
An OBD2 scanner is an essential tool for diagnosing engine problems. It allows you to read the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the ECU, which can provide valuable clues about the cause of the problem.
- Innova 3100i: This is a great entry-level OBD2 scanner that can read and clear codes, view live data, and perform basic diagnostics. It's easy to use and affordable, making it a good choice for beginners. Price: $50-$70
- Autel MaxiCOM MK808: This is a more advanced OBD2 scanner that offers a wider range of features, including bidirectional control, advanced diagnostics, and service resets. It's a good choice for experienced mechanics and serious DIYers. Price: $500-$700
- BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool: This scanner connects to your smartphone via Bluetooth and provides detailed diagnostic information, including code definitions, possible causes, and repair tips. It's a convenient and powerful tool for diagnosing engine problems. Price: $100-$120
Fuel Injector Cleaners for Enhanced Fuel System Performance
Fuel injector cleaners can help remove deposits and buildup from fuel injectors, improving fuel flow and engine performance.
- Sea Foam Motor Treatment: Sea Foam is a versatile fuel additive that can be used to clean fuel injectors, carburetors, and other engine components. It's a popular choice among mechanics and DIYers. Price: $10-$15
- Lucas Fuel Injector Cleaner: Lucas Fuel Injector Cleaner is a concentrated formula that is designed to clean fuel injectors and improve fuel economy. It's a good choice for vehicles with high mileage or those that have been sitting for a long time. Price: $8-$12
- Chevron Techron Concentrate Plus Fuel System Cleaner: Techron is a powerful fuel system cleaner that is designed to remove deposits from fuel injectors, intake valves, and combustion chambers. It's a good choice for vehicles that are experiencing performance problems due to fuel system deposits. Price: $10-$15
Multimeters for Sensor Testing and Electrical Troubleshooting
A multimeter is an essential tool for testing engine sensors and troubleshooting electrical problems.
- Fluke 115: Fluke is a well-known brand that produces high-quality multimeters. The Fluke 115 is a reliable and accurate multimeter that is suitable for a wide range of automotive applications. Price: $150-$200
- Klein Tools MM400: Klein Tools is another reputable brand that produces durable and reliable multimeters. The Klein Tools MM400 is a good choice for automotive use, offering a variety of features at an affordable price. Price: $50-$70
- INNOVA 3320: This multimeter is a budget-friendly option that still offers a good range of features for automotive diagnostics. It's easy to use and suitable for basic testing of sensors and electrical circuits. Price: $20-$30
Preventative Maintenance for Optimal Engine Performance
The best way to avoid engine performance problems is to perform regular preventative maintenance. This includes:
- Changing your engine oil and filter regularly.
- Replacing your air filter regularly.
- Replacing your fuel filter regularly.
- Replacing your spark plugs at the recommended intervals.
- Inspecting your engine belts and hoses for wear and tear.
- Checking your engine coolant level and condition.
By following these tips, you can keep your engine running smoothly and prevent costly repairs down the road. Remember, a well-maintained engine is a happy engine!
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/277019-baked-pork-chops-with-cream-of-mushroom-soup-DDMFS-beauty-4x3-BG-7505-5762b731cf30447d9cbbbbbf387beafa.jpg)